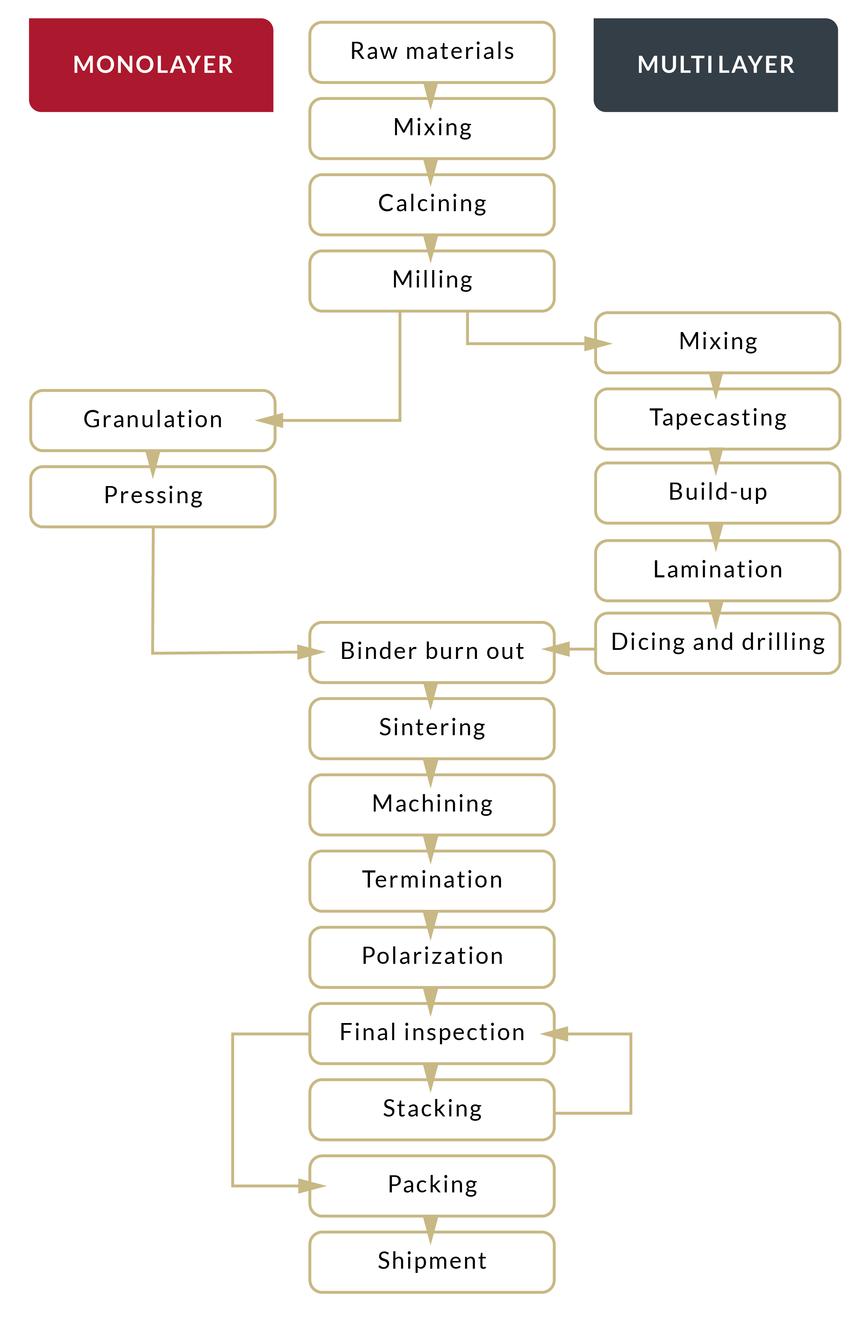
Manufacturing
The manufacturing process for monolayer and multilayer are both the same and quite different. Monolayer is made of one layer of piezoceramic material pressed with up to 1 MN compacting force. Multilayer is made by tape casting very thin layers of piezoceramic material on which thin layers of electrode material is deposited. Approx. 100 layers are then laminated.